本文共 8108 字,大约阅读时间需要 27 分钟。
前言:之前做过的网络socket上报温度是基于TCP。和UDP.HTTP一样都是通信协议,也就是通信时所遵守的规则,只有双方按照这个规则“说话”,对方才能理解或为之服务。这里说的协议,都是基于应用层的协议,一切应用层协议说白了,就是数据包的结构定义。至于TLV格式,就是Type-Length-Value ,数据包里放数据,要么用定长,要么用TLV这种可变长度的。同时TLV是一种通用的socket网络协议数据格式。具有扩展兼容性好,解析快,结构性好,数据包小的特点。
一:TCP HTTP UDP三者的关系:
TCP/IP是个协议组,可分为四个层次:网络接口层、网络层、传输层和应用层。 在网络层有IP协议、ICMP协议、ARP协议、RARP协议和BOOTP协议。 在传输层中有TCP协议与UDP协议。 在应用层有FTP、HTTP、TELNET、SMTP、DNS等协议。 因此,HTTP本身就是一个协议,是从Web服务器传输超文本到本地浏览器的传送协议。二:socket:
这是为了实现以上的通信过程而建立成来的通信管道,其真实的代表是客户端和服务器端的一个通信进程,双方进程通过socket进行通信,而通信的规则采用指定的协议。socket只是一种连接模式,不是协议,tcp,udp,简单的说(虽然不准确)是两个最基本的协议,很多其它协议都是基于这两个协议如,http就是基于tcp的,.用socket可以创建tcp连接,也可以创建udp连接,这意味着,用socket可以创建任何协议的连接,因为其它协议都是基于此的。三:数据包TLV的设计
从应用层HTTP协议,到超文本置标语言HTML(HyperText Mark-up Language),再到可扩展置标语言XML(Extensible Markup Language),它们提供了数据的格式化存储、传输和格式化显示的规范,是网络通信的基石。然而HTTP协议以及HTML/XML置标语言的本质就是定义一堆标签(Tag)对数据进行串行化序列化,然后接收方再根据标签解析、还原数据。自定义通信协议的关键是对数据包的合理构造(construct)和正确解析(parse),即制定编解码规则。
抽象语法标记 ASN(Abstract Syntax Notation) BER的长度确定的编码方式,由3部分组成Identifier octets、Length octets和Contents octets,实际上这就是一种TLV(Type-Length-Value)模型:类型字段(Type或Tag)是关于标签和编码格式的信息;长度字段(Length)定义数值的长度; 内容字段(Value)表示实际的数值。
因此,一个编码值又称TLV三元组。编码可以是基本型或结构型,如果它表示一个简单类型的、完整的显式值,那么编码就是基本型(primitive);如果它表示的值具有嵌套结构,那么编码就是结构型 (constructed)。
TLV编码就是指对Type(Tag)、Length和Value进行编码,形成比特流;解码是编码的逆过程,是从比特流缓冲区中解析还原出原始数据。
参考博客:
客户端数据装包思路:
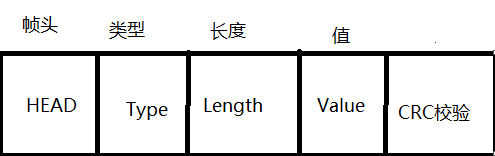 当然中间的T.L.V可以自己随意定义,这个根据自己的实际需求来。 一张图大家应该能看明白: ID:LSJ 3bytes 时间:原本应该为2019-04-18 21:52:37 2019=119(+1900) 数据包: 119 4 18 21 52 37 6bytes 温度:原本应该为19.56℃ 数据包:19 56 2bytes 装包过程明白了原理就很好写
当然中间的T.L.V可以自己随意定义,这个根据自己的实际需求来。 一张图大家应该能看明白: ID:LSJ 3bytes 时间:原本应该为2019-04-18 21:52:37 2019=119(+1900) 数据包: 119 4 18 21 52 37 6bytes 温度:原本应该为19.56℃ 数据包:19 56 2bytes 装包过程明白了原理就很好写  装包代码:
装包代码: #define HEAD 0xFD#define ID 0X01#define INT_TIME 0X02#define FLOAT_TEMP 0X03int makepack(char *buf,int size){ int id_len=0; int data_len=0; int time_len=0; int temp_len=0; int buf_place=0; int i; char *id="lsj"; char datatime[32]; float temp; unsigned short crc16=0; if(!buf || size<18) { printf("Invalid input arguements\n"); return 0; } buf[buf_place]=HEAD; buf_place+=1; data_len=11; buf[buf_place]=data_len; buf_place+=1; buf[buf_place]=ID; buf_place+=1; id_len=strlen(id); memcpy(&buf[buf_place],id,id_len); buf_place+=id_len; buf[buf_place]=INT_TIME; buf_place+=1; memset(datatime,0,sizeof(datatime)); int time=getdatatime(datatime); time_len=time; printf("time_len is %d\n",time_len); for(int i=0;i CRC校验代码直接网上找的,直接套用。没有深入去了解它。大家有兴趣可以去了解。
四:数据包解包
数据包解包的流程就是装包的逆过程,流程图如下: 第一次使用yed画流程图,有点糙,哈哈哈 源代码如下: 这里使用了大量的memmove函数,大家可以去了解一下这个函数
第一次使用yed画流程图,有点糙,哈哈哈 源代码如下: 这里使用了大量的memmove函数,大家可以去了解一下这个函数 #include "tlv.server.h"#include "tlv.crc.h"#define HEAD 0xFD#define ID 0X01#define INT_TIME 0X02#define FLOAT_TEMP 0X03static sqlite3 *db;int dividepack(char *buf,int size){ int i; unsigned short crc16=0; char user[32]; int year; int month; int day; int hour; int minute; int second; int temp_1; int temp_2; int rc; char *db_name="TEMP.db"; char *error=0; char *insert=(char*)malloc(256); char *select="select * from TEMP;"; char *sql="CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS TEMP(""ID INT PRIMARY KEY," "USER CHAR(10)," "TIME CHAR(50)," "TEMP CHAR(10));"; memset(user,0,sizeof(user)); if(!buf||size<=6) { printf("Invalid input arguements\n"); return 0; }flag1:if(size>6) { flag2:for(i=0;i 5) { if(buf[i+1]==11) { if(buf[i+2]==ID) { memcpy(user,&buf[i+3],3); printf("user is %s\n",user); if(buf[i+6]==INT_TIME) { year=buf[i+7]; year+=1900; printf("year is %d\n",year); month=buf[i+8]; printf("month is %d\n",month); day=buf[i+9]; printf("day is %d\n",day); hour=buf[i+10]; printf("hour is %d\n",hour); minute=buf[i+11]; printf("minute is %d\n",minute); second=buf[i+12]; printf("second is %d\n",second); if(buf[i+13]==FLOAT_TEMP) { temp_1=buf[i+14]; printf("temp_1 is %d\n",temp_1); temp_2=buf[i+15]; printf("temp_2 is %d\n",temp_2); crc16=crc_itu_t(MAGIC_CRC,buf,18); //ushort_to_bytes(&buf[i+16],crc16); if(crc16==0) { printf("crc true\n"); printf("divide pack finish\n"); memmove(buf,&buf[i],size);size=0; } else { memmove(buf,&buf[i+16],size-i-16);size=size-i-16;goto flag1; } } else { memmove(buf,&buf[i+13],size-i-13);size=size-i-13;goto flag1; } } else { memmove(buf,&buf[i+6],size-i-6);size=size-i-6;goto flag1; } } else { memmove(buf,&buf[i+2],size-i-2);size=size-i-2;goto flag1; } } else { memmove(buf,&buf[i+1],size-i-1);size=size-i-1;goto flag1; } } else { memmove(buf,&buf[i],size-i);return size-i;goto flag1; } } else { goto flag2; } } } else { return size; } 下面部分是数据库的内容
rc=sqlite3_open(db_name,&db); if(rc!=SQLITE_OK) { fprintf(stderr,"sql error:%s\n",sqlite3_errmsg(db)); } else { printf("open sqlite successfully!\n"); } rc=sqlite3_exec(db,sql,NULL,NULL,&error); if(rc!=SQLITE_OK) { fprintf(stderr,"sql error:%s\n",error); sqlite3_close(db); sqlite3_free(error); exit(1); } else { printf("create table successfully!\n"); } snprintf(insert,256,"insert into TEMP(USER,TIME,TEMP)values('%s','%04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d','%d.%d');",user,year,month,day,hour,minute,second,temp_1,temp_2); rc=sqlite3_exec(db,insert,NULL,NULL,&error); if(rc!=SQLITE_OK) { fprintf(stderr,"sql error:%s\n",error); sqlite3_close(db); sqlite3_free(error); exit(1); } else { printf("insert successfully!\n"); } rc=sqlite3_exec(db,select,NULL,NULL,&error); if(rc!=SQLITE_OK) { fprintf(stderr,"sql error:%s\n",error); sqlite3_close(db); sqlite3_free(error); exit(1); } else { printf("select successfully!\n"); } sqlite3_close(db);} 后序:这篇博客重点在于理解tlv是干嘛的,有什么作用,以及如何运用它。还有要熟练掌握网络socket编程。
项目源码已上传码云:
转载地址:http://ufhgn.baihongyu.com/